Introduction
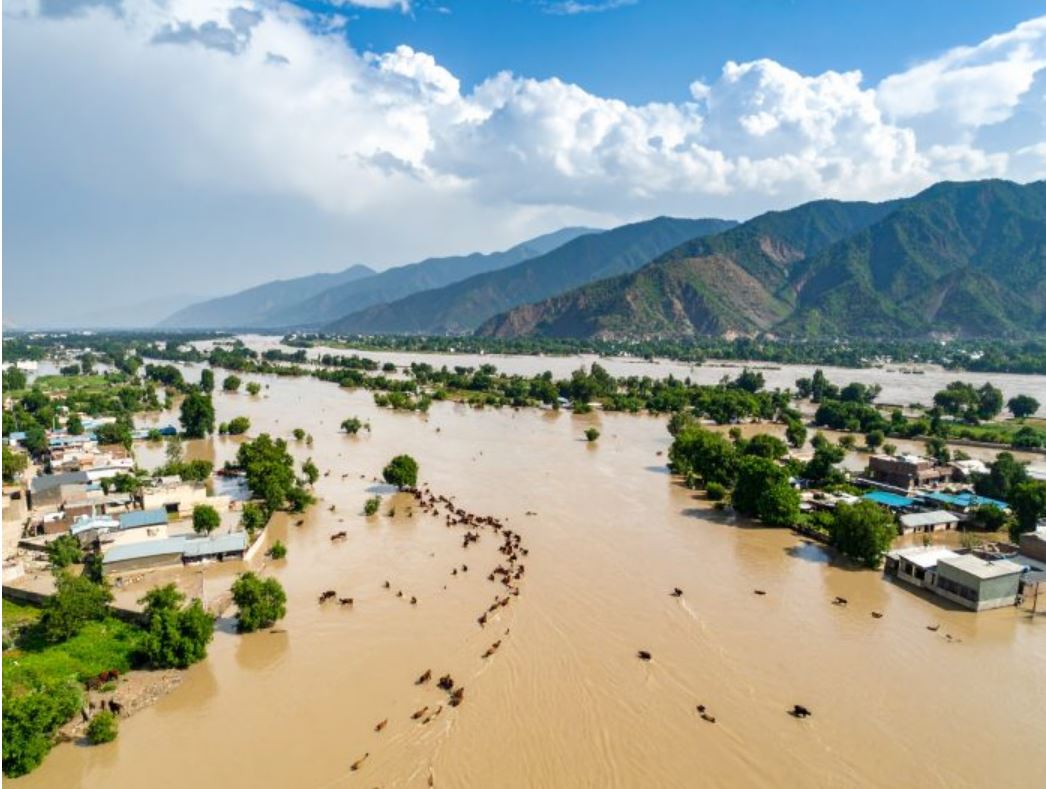
Pakistan is a country blessed with rivers, fertile plains, and diverse landscapes. However, these geographical features also make it prone to recurring floods. In recent years, climate change has intensified this risk, and the Pakistan floods of 2025 once again highlighted the country’s vulnerability to natural disasters. Heavy monsoon rains, melting glaciers in the north, and poor infrastructure led to widespread flooding, affecting millions of people, destroying homes, and leaving a lasting mark on the economy and environment.
This blog explores the causes, impacts, and recovery measures of the 2025 floods in Pakistan, along with long-term solutions to mitigate future disasters.
Causes of Floods in Pakistan 2025
Flooding in Pakistan is not new, but in 2025 several factors combined to create a large-scale disaster:
1. Climate Change and Extreme Weather
Unpredictable and heavy monsoon rains were a major trigger. Climate change has altered rainfall patterns, making storms more intense and frequent. This sudden downpour overwhelmed riverbanks and urban drainage systems.
2. Glacial Melting in the North
Pakistan has more than 7,000 glaciers, many of which are rapidly melting due to rising global temperatures. This leads to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) that pour into rivers, raising water levels beyond control.
3. Poor Urban Planning
Rapid, unplanned urbanization has blocked natural drainage channels. Cities like Karachi, Lahore, and Islamabad saw severe waterlogging because of encroachments and lack of proper sewage systems.
4. Deforestation and Soil Erosion
Widespread deforestation in northern and central regions has reduced the land’s capacity to absorb rainwater. Without trees to hold soil together, floodwaters flow faster and cause more destruction.
5. Weak Infrastructure and Dams
Pakistan’s dam and canal system is outdated. Insufficient water storage and weak embankments failed to hold back rising waters, resulting in massive overflow.
🌊 Pakistan Floods 2025: Causes, Impact, and Recovery Measures
Impact of Floods in Pakistan 2025
The floods of 2025 brought devastation across multiple sectors:
1. Humanitarian Crisis
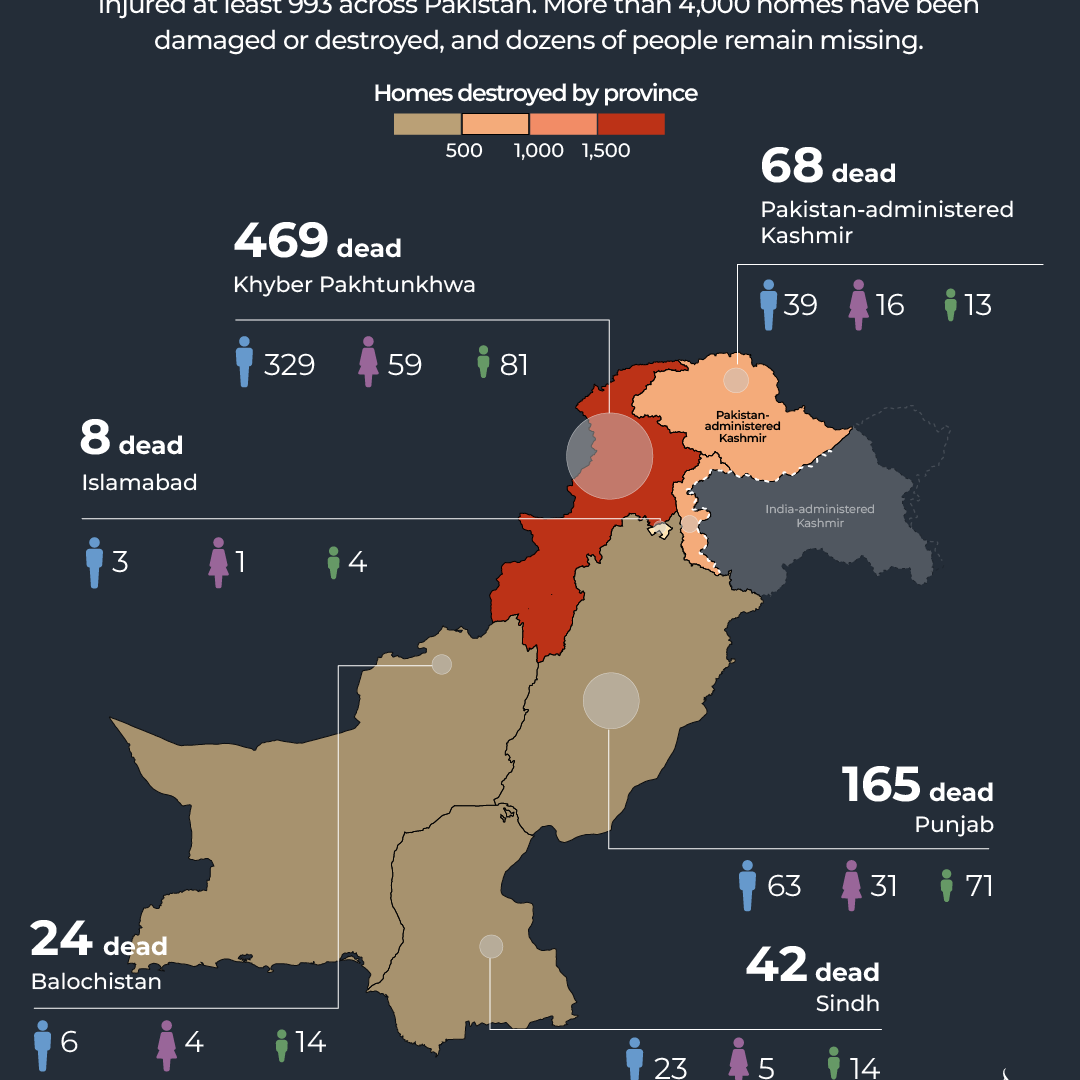
- Over 10 million people were directly affected.
- Thousands lost their homes and were forced into temporary shelters.
- Shortages of clean drinking water led to health crises like cholera and dengue fever outbreaks.
2. Agricultural Losses
Pakistan’s economy depends heavily on agriculture. The floods destroyed standing crops of rice, wheat, and sugarcane across Punjab and Sindh. Livestock deaths added to farmers’ losses, pushing many into poverty.
3. Economic Damage
- Billions of rupees worth of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and schools, were damaged.
- Trade routes were disrupted, increasing inflation.
- The World Bank estimated losses of over $10 billion, making it one of the costliest natural disasters in Pakistan’s history.
4. Environmental Consequences
Floodwaters caused soil erosion, loss of fertile land, and contamination of freshwater sources. Ecosystems and wildlife habitats were also disturbed.
5. Psychological and Social Impact
Natural disasters not only cause physical damage but also trauma. Families lost loved ones, communities were displaced, and thousands of children lost access to education.
Recovery and Relief Measures
Despite challenges, Pakistan initiated several measures to recover from the 2025 floods:
1. Emergency Relief Operations
The Pakistan Army, NGOs, and international organizations provided rescue operations, food supplies, and temporary shelters. Helicopters were deployed to reach stranded communities.
2. International Aid
Countries and organizations like the UN, World Bank, and Red Crescent extended financial and humanitarian support. Relief funds helped restore basic infrastructure and assist flood victims.
3. Rehabilitation Programs
Government programs focused on rebuilding schools, hospitals, and homes. Cash compensation was provided to affected families, although many complained about delays and corruption.
4. Health and Sanitation Campaigns
Medical camps were established to fight waterborne diseases. Awareness campaigns encouraged safe drinking water practices and vaccinations.
5. Agricultural Support
Farmers were provided with seeds, fertilizers, and livestock assistance to recover their livelihoods. Some regions received subsidies to rebuild farmlands.
Long-Term Solutions to Prevent Future Floods
To reduce the devastation of future floods, Pakistan must take sustainable preventive measures:
✅ 1. Improve Water Management
- Build new dams and reservoirs for better water storage.
- Strengthen canal systems and river embankments.
✅ 2. Urban Planning and Drainage Systems
- Modernize drainage infrastructure in cities.
- Enforce strict laws against illegal construction on floodplains.
✅ 3. Reforestation Campaigns
- Plant trees across riverbanks and hilly areas.
- Launch nationwide tree plantation drives to improve soil absorption.
✅ 4. Early Warning Systems
- Use AI and satellite technology for real-time flood predictions.
- Develop community-level awareness programs for disaster preparedness.
✅ 5. Climate Change Adaptation
- Reduce carbon emissions and promote renewable energy.
- Collaborate internationally to address the global climate crisis.
Conclusion
The Pakistan floods of 2025 serve as a reminder that natural disasters are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change and human negligence. While immediate relief efforts saved lives, long-term planning is essential to prevent such devastation in the future.
By focusing on better water management, sustainable urban planning, reforestation, and climate adaptation, Pakistan can minimize the risks of flooding and protect its people, economy, and environment. Floods may be natural, but their impact can be reduced through human effort, awareness, and unity.



