Difference Between Blue and Black Solar Panels: Which One Should You Choose
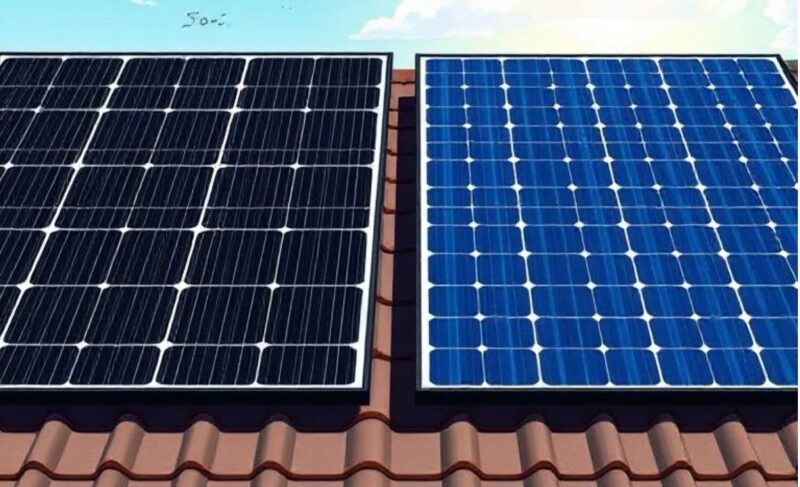

Solar panels have become an essential investment for homeowners and businesses looking to harness renewable energy. When choosing solar panels, one of the most noticeable distinctions is their color—blue or black. While this may seem like a mere aesthetic difference, the color actually signifies variations in the technology, efficiency, cost, and overall performance of the panels. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision when investing in solar energy.
1. The Science Behind the Colors
The difference in color between blue and black solar panels comes from their composition and manufacturing process.
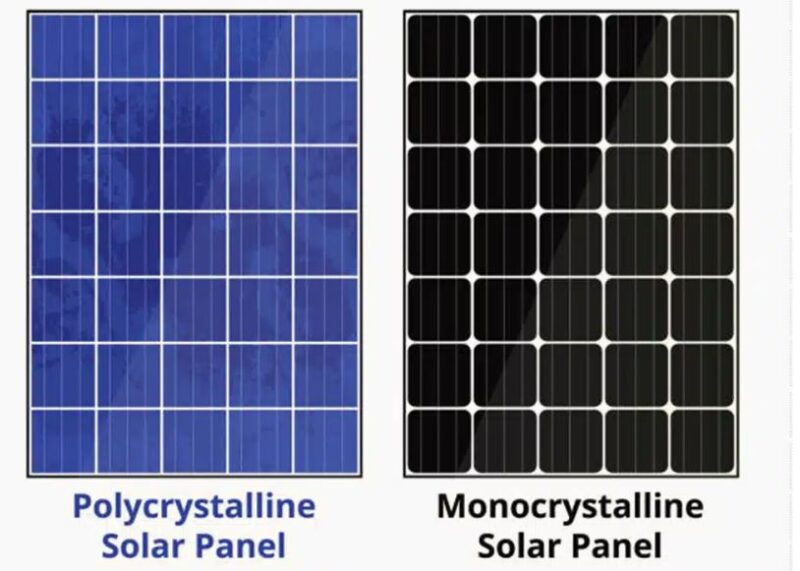
Blue Solar Panels (Polycrystalline)
Blue solar panels are made using polycrystalline silicon. This manufacturing process involves melting together multiple fragments of silicon and allowing them to cool and solidify into a panel. This process forms multiple silicon crystals within each cell, giving the panel its characteristic blue hue.
Black Solar Panels (Monocrystalline)
Black solar panels are made from monocrystalline silicon. This means that the silicon used is derived from a single continuous crystal structure. The monocrystalline silicon absorbs light more efficiently, which results in a uniform black appearance. The process of manufacturing these panels is more complex and energy-intensive.
2. Efficiency and Performance
The efficiency of a solar panel determines how much sunlight is converted into electricity.
- Monocrystalline Panels (Black): These panels tend to be more efficient, typically exceeding 20% efficiency. Their uniform crystal structure allows for better electron flow, improving energy conversion. This makes black solar panels ideal for small spaces where you need to maximize energy output.
- Polycrystalline Panels (Blue): These panels generally have lower efficiency, ranging between 13% to 16%. Because they are made of multiple silicon crystals, the boundaries between these crystals can hinder the movement of electrons, reducing efficiency. However, they can still be a good choice for areas with abundant space for installation.
3. Cost Differences
Cost is a major factor when choosing solar panels.
- Blue Panels (Polycrystalline): The production of polycrystalline panels is simpler and more cost-effective, making them a more affordable option. If you are on a budget and have sufficient roof space, blue solar panels may be the right choice.
- Black Panels (Monocrystalline): The manufacturing process of black solar panels is more complex and requires higher-quality silicon, which makes them more expensive. However, their higher efficiency can make them a cost-effective long-term investment.
4. Durability and Lifespan
Both types of solar panels are built to last, but their durability may differ slightly.
- Black Panels (Monocrystalline): These panels tend to have a longer lifespan, often lasting 25–30 years or more. They also come with longer warranties, reflecting their higher durability.
- Blue Panels (Polycrystalline): These panels also have a long lifespan, typically between 20–25 years. However, they may degrade slightly faster than monocrystalline panels over time.
5. Aesthetic Appeal
Aesthetics can be a crucial factor, especially for homeowners who want their solar panels to blend in with their roof design.
- Black Panels: Their sleek, uniform look makes them more visually appealing. They tend to blend well with darker roofs and modern architectural styles.
- Blue Panels: The speckled blue appearance of polycrystalline panels may stand out more, which can be a disadvantage if aesthetics are a priority.
- 6. Performance in Different Environments
Different solar panel types perform differently under various environmental conditions.
- Monocrystalline Panels (Black): These panels perform better in low-light conditions and high temperatures. They have a lower temperature coefficient, meaning they maintain efficiency even in hot weather.
- Polycrystalline Panels (Blue): These panels are more affected by high temperatures, which can slightly reduce their efficiency on very hot days.
7. Space Requirements
If you have limited roof space, the efficiency of your solar panels becomes an even more significant factor.
- Black Panels: Because they are more efficient, you will need fewer black solar panels to generate the same amount of electricity.
- Blue Panels: Since they are less efficient, you may require more panels to meet your energy needs.
8. Environmental Impact
The production of solar panels has an environmental footprint, but some panels are more sustainable than others.
- Polycrystalline Panels (Blue): These have a lower energy consumption during manufacturing, making them a slightly more environmentally friendly option.
- Monocrystalline Panels (Black): The manufacturing process for monocrystalline panels consumes more energy and generates more waste, making them slightly less eco-friendly than their blue counterparts.
9. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient indicates how much a solar panel’s efficiency decreases as the temperature rises.
- Monocrystalline Panels: Have a lower temperature coefficient, meaning they perform better in extreme heat.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Are more affected by heat, which can reduce their overall efficiency in very hot climates.
10. Market Availability and Future Trends
- Monocrystalline Panels: As solar technology advances, monocrystalline panels are becoming more widely available and increasingly affordable.
- Polycrystalline Panels: While still popular, the market is shifting toward monocrystalline panels due to their superior efficiency and performance.
Which One Should You Choose?
Your choice between blue and black solar panels depends on several factors:
- Budget: If you are looking for a cost-effective solution, blue polycrystalline panels may be the best choice.
- Space Constraints: If you have limited space, black monocrystalline panels are more efficient and will require fewer panels.
- Aesthetic Preference: If you want a sleek and modern look, black solar panels are the better option.
- Climate: If you live in a region with high temperatures, black solar panels will perform better.
- Long-Term Investment: If you are looking for higher efficiency and longer durability, monocrystalline panels are the best choice.
Conclusion
Both blue and black solar panels have their advantages and disadvantages. Blue solar panels are more affordable but less efficient, making them ideal for large spaces with budget constraints. Black solar panels are more expensive but offer better efficiency, durability, and aesthetic appeal, making them a great long-term investment. By considering factors like budget, space, climate, and personal preferences, you can make an informed decision that best suits your solar energy needs.